How to Provide Remote Access to External Identities to the Organization?
1. Third Party
A Third Party is an identity with which, as an organization, you are required to work and to whom you must provide the technical means to intervene on your IT system. This identity can be:
- Software vendor
- B2B company (Service provider)
- Help Desk (Intervention)
- Technician (Maintenance, Update)
Summary: Third Parties are multiple individuals, can be anywhere in the world, and need access to critical resources of the company.
2. Business Issues
In an organization, employees have accounts (digital identities) that allow them to access privileged resources. To be protected and controlled, these personal accounts benefit from multiple levels of protection (Least Privilege / Password Policy, etc.).
These different levels of protection require the organization and employees to maintain impeccable digital hygiene to ensure the security of these digital identities (password management, rights management).
When creating a company account, several levels of access and privileges must be assigned so that the employee can work. Many of these accesses and privileges are inherent to having an account within the organization, and are not trivial for your company’s security:
- Access to the company directory
- Access to the company network
- Company VPN
- Company computer
While for internal employees or contracted service providers this does not pose a direct risk, what about Third Parties?
Here are some questions that can help you mature their management:
- Are my Third Parties identified? (duration of intervention, visibility on external identities)
- How do you manage their occasional interventions? (Remote access, on-site travel, deployment of a VPN on their external workstation, provision of an internal workstation)
- How do you manage their identities? (Account creation process, account deletion process)
- What level of privilege and trust is granted to them? (Permissions and privileges)
- When the organization wants to involve an external service provider (Third Party), how do you control the actions performed? (File transfer, use of privileged accounts)
3. Architecture
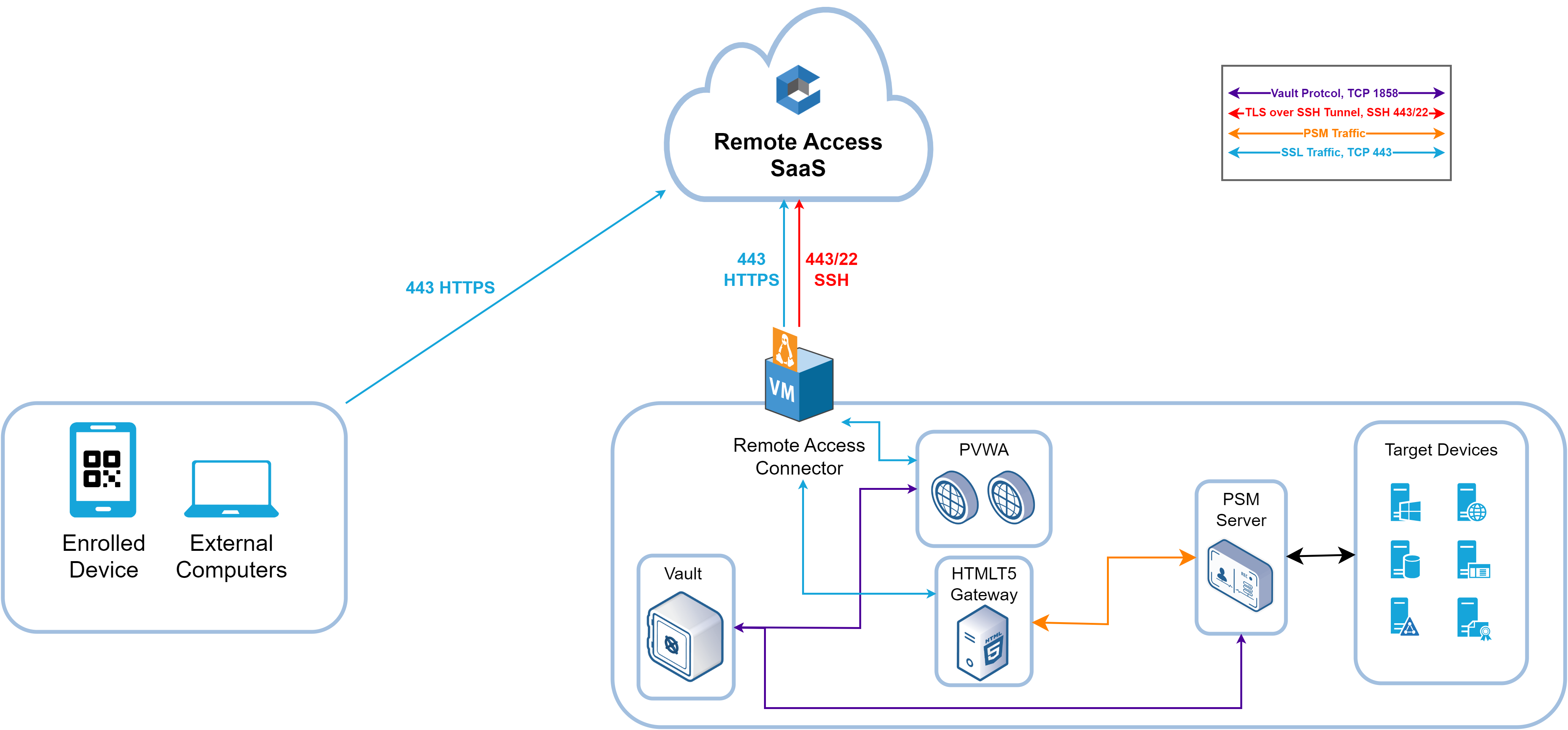
4. How Does CyberArk Remote Access Work?
- The user launches the CyberArk Mobile application with which they have been enrolled.
- They load the CyberArk Remote Access tenant linked to their region (Europe, America, etc.).
- They scan the QR code linked to the organization’s tenant and get connected.
- Once connected, they can load any application shared by the company (e.g., PVWA).
- They access the company’s PVWA and can connect to the privileged targets shared by the organization.
- They connect through the HTML5 GW + PSM.
5. What are the Benefits?
Limit Security Risks
- Zero Trust and JIT Access
- No password, token
Reduce Cost and Operational Complexity
- SaaS solution
- Automation
Simplify Remote Access
Improve Visibility and Compliance
- Monitor privileged access in real-time
- Detect potential attacks
- Compliance reporting